Description
Buy MET Fumarate (N-methyl-N-ethyltryptamine) Online
Buy MET Fumarate (N-methyl-N-ethyltryptamine) online. MET is a substance that is only sold for research purposes and is therefore not intended for consumption.
MET retains its stability for up to 2 years when stored in the correct environment. MET is intended for research purposes and not for consumption. That is why it is important that the product is kept out of the reach of children and pets.
We offer good quality research chemicals at a fair price. Your order will be shipped every day within 24 hours. Therefore, order MET N-Methyl-N-ethyltryptamine fumarate safely and quickly via chemstoreonline.com!
MET fumarate properties
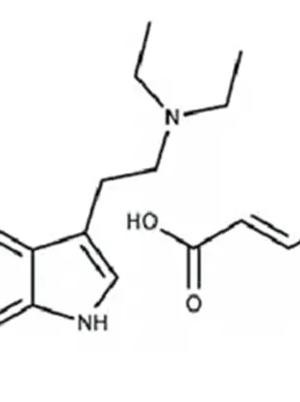
Synonym: N-methyl-N-ethyltryptamine fumarate
CAS Number: 5599-69-9
Formula: 3-[2-(ethyl(methyl)amino)ethyl]-1H-indole fumarate
Mole mass: 318.4 g/mol
Purity: >97%
What is MET?
MET, also known as N-Methyl-N-ethyltryptamine, is a research chemical that belongs to the
tryptamine class. It is a compound that has aroused scientific interest because of its unique structure and potential pharmacological effects. MET is derived from tryptotamine by adding a methyl group to the amine nitrogen and an ethyl group to the side chain. This change results in a connection with different properties and potential interactions with receptors in the brain.
In scientific studies, MET has shown to be active as a psychedelic compound, meaning it can cause changes in perception, cognition, and mood. Researchers have observed that MET can cause changes in sensory perception, emotional experiences and thought patterns. These effects are thought to occur through the interaction with serotonin receptors, which play a crucial role in regulating mood and cognition.
Research on MET and other research chemicals is conducted in controlled laboratory environments by trained scientists and researchers. It is important to note that the use of MET outside of controlled research is strongly discouraged, as the effects and possible risks are not fully understood.
Research on MET is aimed at deepening our understanding of the pharmacological properties, receptor interactions and possible therapeutic applications. By studying MET and related compounds, scientists hope to shed light on the mechanisms underlying altered states of consciousness and possibly develop new treatments for various mental illnesses.
How did MET come about?
The history of MET dates back to the mid-20th century when it was first synthesized and studied on its effects on the central nervous system. Researchers were intrigued by the similarities between MET and other tryptamine compounds, such as serotonin and melatonin, which play an important role in regulating mood, cognition, and various physiological processes.
As a research chemical, MET has been
studied mainly because of its potential psychoactive properties. Studies have shown that it can cause changes in perception, mood and cognition, similar to other psychedelic substances. MET is believed to interact with specific receptors in the brain, particularly serotonin receptors, which are known to modulate various neurological functions.
The research into MET and its effects is an ongoing process in the field of psychopharmacology and neuroscience. Researchers are interested in understanding the mechanisms of action of MET and its potential therapeutic applications. By studying MET and related connections, scientists want to deepen our knowledge of the brain and its complex interactions, which ultimately contributes to advances in the research into and treatment of mental health
.Hazard indication
MET can cause respiratory irritations
MET can cause irritations in the eyes.
Research chemicals discharge into the environment is prohibited.
IN CONTACT WITH THE EYES: Gently rinse the eyes with water for five minutes. Remove the contact lenses if possible.
IN CONTACT WITH THE SKIN: Wash the skin with soap and water.
AFTER BREATHING WITH: bring the victim into the fresh air and leave the victim in a posture that makes breathing easy.



Reviews
There are no reviews yet.